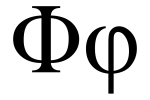Phi
From Textus Receptus
m (Protected "Phi" [edit=autoconfirmed:move=autoconfirmed]) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | [[Image:Phi.png|thumb|150px|Phi]] | |
| + | '''Phi''' (uppercase Φ, lowercase φ or math symbol ϕ), pronounced ˈfaɪ or sometimes /ˈfiː/ in English,<sup>[]</sup> and ˈfi in [[Modern Greek language|modern Greek]], is the 21st letter of the [[Greek alphabet]]. In modern Greek, it represents [f], a [[voiceless labiodental fricative]]. In Ancient Greek it represented [pʰ], an [[Aspiration (phonetics)|aspirated]] [[voiceless bilabial plosive]] (from which English ultimately inherits the spelling "[[ph (digraph)|ph]]" in words derived from Greek). In the system of [[Greek numerals]] it has a value of 500 (φʹ) or 500,000 (͵φ). The Cyrillic letter [[Ef (Cyrillic)|Ef]] (Ф, ф) arose from Φ. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Use as a symbol == | ||
| + | The lower-case letter <math>\varphi \,</math> (or often its variant, <math>\phi \,</math>) is often used to represent the following: | ||
| + | *The [[golden ratio]] <math>\tfrac{1 + \sqrt{5}}{2} \approx 1.61803\ldots</math> in mathematics, art, and architecture. | ||
| + | *[[Euler's totient function]] ''φ''(''n'') in number theory; also called ''Euler's phi function''. | ||
| + | *In algebra, [[Group (mathematics)|group]] or [[Ring (mathematics)|ring]] [[homomorphism]]s | ||
| + | * In [[probability theory]], {{nowrap|1=''ϕ''(''x'') = (2π)<sup>−½</sup>''e''<sup>−''x''<sup>2</sup>/2</sup>}} is the [[probability density function]] of the [[normal distribution]]. | ||
| + | * In [[probability theory]], {{nowrap|1=''φ''<sub>''X''</sub>(''t'') = E[ ''e''<sup>''itX''</sup> ]}} is the [[characteristic function (probability theory)|characteristic function]] of a random variable ''X''. | ||
| + | *An [[angle]], typically the second angle mentioned, after ''θ'' ([[theta]]). Especially: | ||
| + | **The argument of a [[complex number]]. | ||
| + | **The [[phase (waves)|phase of a wave]] in signal processing. | ||
| + | **In [[spherical coordinates]], mathematicians usually refer to phi as the polar angle (from the ''z''-[[Coordinate axis|axis]]). The convention in physics is to use phi as the azimuthal angle (from the ''x''-axis). | ||
| + | **One of the [[dihedral angle]]s in the backbones of [[protein]]s. | ||
| + | **Internal or effective [[angle of friction]]. | ||
| + | *[[Electric potential]] in physics. | ||
| + | *The [[work function]] in electronics. | ||
| + | *A [[shorthand]] representation for an [[aromatic]] [[functional group]] in [[organic chemistry]]. | ||
| + | *The [[fugacity]] coefficient in [[thermodynamics]]. | ||
| + | *The ratio of [[Thermodynamic free energy|free energy]] destabilizations of protein [[mutant]]s in [[phi value analysis]]. | ||
| + | *In [[cartography]] and [[navigation]], [[latitude]]. | ||
| + | *In combustion engineering, equivalence ratio. The ratio between the actual fuel air ratio to the stoichiometric fuel air ratio. | ||
| + | *A sentence in [[first-order logic]]. | ||
| + | *[[Porosity]] in geology and [[hydrology]]. | ||
| + | *Strength (or resistance) reduction factor in [[structural engineering]], used to account for statistical variabilities in materials and construction methods. | ||
| + | *The symbol for a [[voiceless bilabial fricative]] in the [[International Phonetic Alphabet]] (using the straight line variant character) | ||
| + | *In economics, this is usually an additive term.{{Clarify|date=October 2009}} | ||
| + | *In [[flight dynamics]], the roll angle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The upper-case letter Φ is used as a symbol for: | ||
| + | *The [[Golden_ratio#Golden_ratio_conjugate|golden ratio conjugate]] −0.618... in mathematics. | ||
| + | *The [[magnetic flux]] and [[electric flux]] in physics, with subscripts distinguishing the two. | ||
| + | *The [[cumulative distribution function]] of the [[normal distribution]] in [[mathematics]] and [[statistics]]. | ||
| + | *[[Philosophy]]. | ||
| + | *The number of phases in a power system in [[electrical engineering]], for example 1Φ for [[single phase]], 3Φ for [[three phase]]. | ||
| + | *A common symbol for the parametrization of a surface in vector [[calculus]]. | ||
| + | *In [[Lacanian algebra]], Φ stands for the imaginary phallus and also represents phallic signification. -Φ stands in for castration.<sup>[]</sup> | ||
| + | The [[diameter]] symbol in [[engineering]], [[⌀]], is often incorrectly referred to as "phi". This symbol is used to indicate the diameter of a circular section, for example "⌀14", means the diameter of the [[circle]] is 14 [[Units of measurement|units]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | *[[F|F, f - Ef (Latin)]] | ||
| + | *[[Ef (Cyrillic)|Ф, ф - Ef (Cyrillic)]] | ||
| + | *[[Psi and phi type figurine]] | ||
| + | * [[Փ]] ([[Armenian alphabet|Armenian letter]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{DEFAULTSORT:Phi (Letter)}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Greek letters]] | ||
Revision as of 03:55, 2 April 2011
Phi (uppercase Φ, lowercase φ or math symbol ϕ), pronounced ˈfaɪ or sometimes /ˈfiː/ in English,[] and ˈfi in modern Greek, is the 21st letter of the Greek alphabet. In modern Greek, it represents [f], a voiceless labiodental fricative. In Ancient Greek it represented [pʰ], an aspirated voiceless bilabial plosive (from which English ultimately inherits the spelling "ph" in words derived from Greek). In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 500 (φʹ) or 500,000 (͵φ). The Cyrillic letter Ef (Ф, ф) arose from Φ.
Use as a symbol
The lower-case letter <math>\varphi \,</math> (or often its variant, <math>\phi \,</math>) is often used to represent the following:
- The golden ratio <math>\tfrac{1 + \sqrt{5}}{2} \approx 1.61803\ldots</math> in mathematics, art, and architecture.
- Euler's totient function φ(n) in number theory; also called Euler's phi function.
- In algebra, group or ring homomorphisms
- In probability theory, ϕ(x) = (2π)−½e−x2/2 is the probability density function of the normal distribution.
- In probability theory, φX(t) = E[ eitX ] is the characteristic function of a random variable X.
- An angle, typically the second angle mentioned, after θ (theta). Especially:
- The argument of a complex number.
- The phase of a wave in signal processing.
- In spherical coordinates, mathematicians usually refer to phi as the polar angle (from the z-axis). The convention in physics is to use phi as the azimuthal angle (from the x-axis).
- One of the dihedral angles in the backbones of proteins.
- Internal or effective angle of friction.
- Electric potential in physics.
- The work function in electronics.
- A shorthand representation for an aromatic functional group in organic chemistry.
- The fugacity coefficient in thermodynamics.
- The ratio of free energy destabilizations of protein mutants in phi value analysis.
- In cartography and navigation, latitude.
- In combustion engineering, equivalence ratio. The ratio between the actual fuel air ratio to the stoichiometric fuel air ratio.
- A sentence in first-order logic.
- Porosity in geology and hydrology.
- Strength (or resistance) reduction factor in structural engineering, used to account for statistical variabilities in materials and construction methods.
- The symbol for a voiceless bilabial fricative in the International Phonetic Alphabet (using the straight line variant character)
- In economics, this is usually an additive term.Template:Clarify
- In flight dynamics, the roll angle.
The upper-case letter Φ is used as a symbol for:
- The golden ratio conjugate −0.618... in mathematics.
- The magnetic flux and electric flux in physics, with subscripts distinguishing the two.
- The cumulative distribution function of the normal distribution in mathematics and statistics.
- Philosophy.
- The number of phases in a power system in electrical engineering, for example 1Φ for single phase, 3Φ for three phase.
- A common symbol for the parametrization of a surface in vector calculus.
- In Lacanian algebra, Φ stands for the imaginary phallus and also represents phallic signification. -Φ stands in for castration.[]
The diameter symbol in engineering, ⌀, is often incorrectly referred to as "phi". This symbol is used to indicate the diameter of a circular section, for example "⌀14", means the diameter of the circle is 14 units.