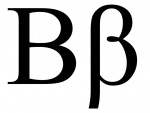Vita (letter)
From Textus Receptus
Vita (uppercase Β, lowercase β, internal ϐ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In high-quality print, the variant of the lowercase letter without a descender is used within a word: βίβλος is printed |βίϐλος. The form ‹ϐ› is very common in handwriting.
The name of the letter is pronounced /ˈbeɪtə/ (US) or /ˈbiːtə/ (UK), and in Greek βήτα ˈvita.
In the system of Greek numerals Beta has a value of 2.
Contents |
History
The letter Beta was derived from the Phoenician letter Beth ![]() . Letters that arose from Beta include the Roman letter ‹B› and the Cyrillic letters ‹Б› and ‹В›.
. Letters that arose from Beta include the Roman letter ‹B› and the Cyrillic letters ‹Б› and ‹В›.
Uses
Ancient Greek
In Ancient Greek, Beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive /b/. The name of the letter, βῆτα bêta, was pronounced bɛ̂ːta.
Modern Greek
In Modern Greek, Beta represents the voiced labiodental fricative v/. The name of the letter is spelled βήτα in the modern monotonic orthography, and pronounced ˈvita.
Math and science
Beta is often used to denote a variable in mathematics and physics, where it often has specific meanings for certain applications, such as representing beta radiation. In regression analysis, ‹B› symbolizes non-standardized partial slope coefficients, whereas ‹β› represents standardized (standard deviation-score form) coefficients; in both cases, the coefficients reflect the change in the criterion Y per one-unit change in the value of the associated predictor X.
Finance
Beta is used in finance as a measure of investment portfolio risk.
International Phonetic Alphabet
In the International Phonetic Alphabet, Greek minuscule beta denotes a voiced bilabial fricative [β].
| Majuscule form | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Α | Β | Γ | Δ | Ε | Ζ | Η | Θ | Ι | Κ | Λ | Μ | Ν | Ξ | Ο | Π | Ρ | Σ | Τ | Υ | Φ | Χ | Ψ | Ω | |||||||||
| Minuscule form | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| α | β | γ | δ | ε | ζ | η | θ | ι | κ | λ | μ | ν | ξ | ο | π | ρ | σ | τ | υ | φ | χ | ψ | ω | |||||||||